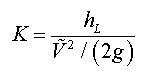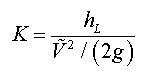Contents
- Index
Minor Losses (Resistance Coefficients) and Flow Measurement
Flow Measurement
Minor Losses
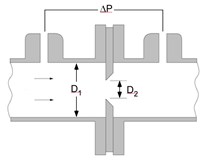
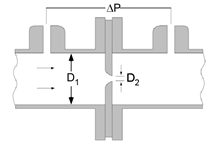
Minor losses refers to the head loss (or pressure losses) occuring in typical piping systems due to steady-state flow through piping components such as fittings, valves, bends, elbows, tees, inlets, outlets, etc. The head loss caused by flow through these components can be represented with a dimensionless resistance coefficient, K, defined as:
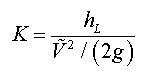
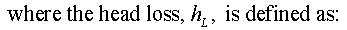
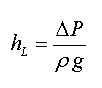
where DP is the pressure loss introduced by the piping component, r is the density, and g is gravitational acceleration.
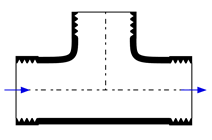
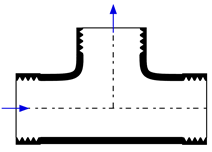
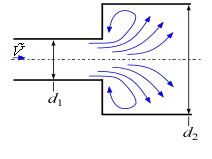
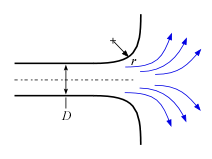
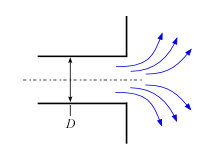
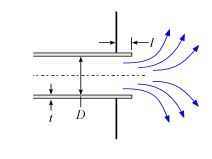
This library file provides the values of resistance coefficients for the pipe components shown below. Click on a picture to obtain information for that component.
Expansions
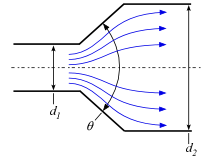
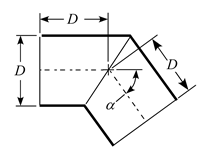
Contractions
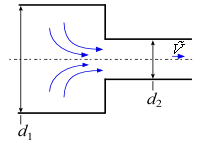
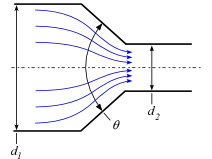
Inlets
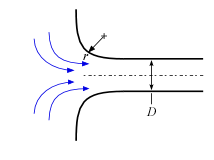
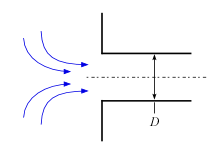
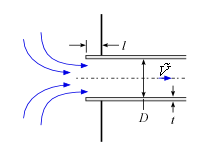
Exits
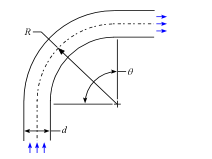
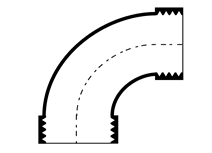
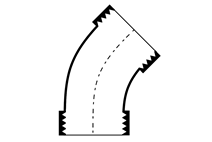
Bends and Elbows
Valves
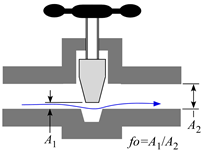
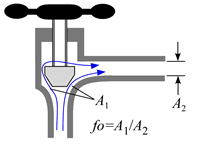
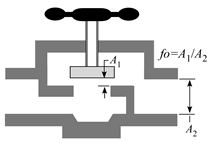
Tees