Contents
CentrifugalPump1_CL
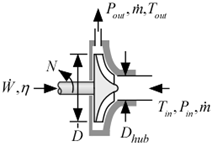
The procedure CentrifugalPump1_CL provides a model of a centrifugal pump that can be used for a real fluid, a brine, or an incompressible fluid. Pumping performance is obtained from a correlation of dimensionless pressure rise as a function of head coefficient curve that is based on data from several manufacturers and pumps. The power performance is obtained from dimensionless power as a function of dimensionless flow curve also based on these data.
Inputs:
F$: fluid string identifier
C: concentration (%) {only used if the fluid is a brine; otherwise set C=0}
T_in: inlet temperature (K, C, F, or R)
P_in: inlet pressure (bar, atm, Pa, kPa, MPa)
m_dot: mass flow rate (kg/s or lb_m/hr)
N: rotational speed (1/s)
D: tip diameter (m or ft)
D_hub: hub diameter (m or ft)
Outputs:
P_out: outlet pressure (bar, atm, Pa, kPa, MPa)
T_out: outlet temperature (K, C, F, or R)
W_dot: power (W, kW or Btu/hr)
eta: efficiency
Example:
$UnitSystem SI Mass J K Pa
C=20 [%]
F$='EG'
T_in=300 [K]
P_in=100000 [Pa]
m_dot=2 [kg/s]
N=1700 [1/min]*convert(1/min,1/s)
D=0.15 [m]
D_hub=0.08 [m]
Call CentrifugalPump1_CL( F$, C, T_in, P_in, m_dot, N, D, D_hub: P_out, T_out, W_dot, eta)
{Solution:
P_out = 211586 [Pa]
T_out = 300 [K]
W_dot = 381.2 [W]
eta= 0.5729}
See also: GearPump1_CL
Reference: O.E. Balje, Turbomachines: A Guide to Design, Selection and Theory, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., (1981), ISBN: 0471060364
Index
