Contents - Index - Previous - Next
S_DEP_PR
S_DEP_PR (Tr, w, Z, B) returns the entropy departure for a pure fluid according to the Peng-Robinson equation of state
where
Tr is reduced temperature
w is the acentric factor
Z is the compressibility factor
B is the second Peng-Robinson equation of state parameter
Entropy departure is the difference in entropy for an ideal gas (designated with the superscript 0) and a real gas at the same temperature and pressure divided by R, the gas constant.
![]()
Note that Z is provided by functions Z_G_PR and Z_L_PR and B is provided by procedure AB_PR for pure fluids.
The entropy departure of a mixture cannot be determined with this function since Tr for a mixture is not defined. Using the Peng-Robinson equation for a mixture, the entropy departure for a mixture can be expressed:
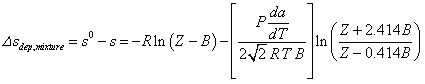
Procedure AB_MIX_PR can be used to determine values of A and B for the mixture and functions Z_G_PR and Z_L_PR provide the value of Z. The value of da/dT for the mixture is provided by function DSADT_MIX_PR.
Example:
Tr=0.85
Pr=0.5
omega=0.05
Call AB_PR(Tr, Pr, omega: A,B)
Z_G=Z_G_PR(A,B)
R=R#
Tc=190.6 [K] "methane"
DELTAh=H_DEP_PR(Tr,omega,Z_G,B)*R*Tc
DELTAs=S_DEP_PR(Tr,omega,Z_G,B)*R
{Solution:
A=0.3391
B=0.04576
DELTAh=1608 [kJ/kmol]
DELTAs=7.126 [kJ/kmol-K]
omega=0.05
Pr=0.5
R=8.314 [kJ/kmol-K]
Tc=190.6 [K]
Tr=0.85
Z_G=0.5748
}