Contents
- Index
Cond_Tube_Avg
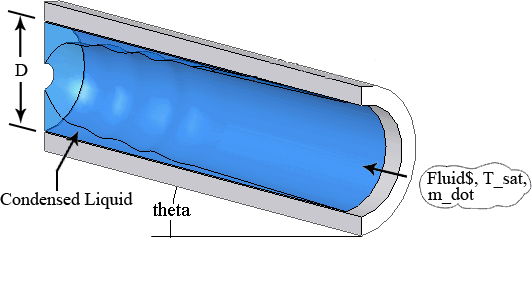
Procedure Cond_Tube_avg(Fluid$, m_dot, T_sat, D, x_1, x_2 : h_m) calculates the average heat transfer coefficient for condensation of vapor entering at quality x_1 as it condenses to a state with quality x_2 inside a circular tube using the correlations from Shah (2016).
Inputs:
Fluid$ - string variable representing a fluid/vapor in the EES data base.
theta - angle of tube between -90° (flow down) and 90° (flow up). Horizontal is 0°.
m_dot - mass flow rate of vapor [kg/s] or [lbm/min]
T_sat - the saturation temperature of the incoming vapor in [C], [K], [F], or [R].
D - inner diameter of the tube in [m] or [ft]
x_1 - entering quality (must be between 0 and 1)
x_2 - exiting quality (must be between 0 and 1)
Outputs:
h_TP_avg - the mean heat transfer coefficient in [W/m^2-K] or [Btu/hr-ft^2-R]
Notes:
This procedure uses the Cond_Tube procedure to supply values for the mean heat transfer coefficient at discrete values of quality. It then integrates these values and returns the average heat transfer coefficient.
Example:
Fluid$='R134a'
x=0.2
m_dot=0.005 [kg/s]
T_sat=50[C]
D=0.01[m]
theta=0[°]
x_1=1
x_2=0
Call Cond_tube_avg(Fluid$, theta, m_dot, T_sat, D, x_1, x_2: h_TP_avg)
{Solution: h_TP_avg=1455 [W/m^2-K]}
Notes:
Procedure Cond_HorizontalTube_avg provides the average heat transfer coefficient for a horizontal tube using alternative correlations. Use of Cond_Tube_Avg is recommended because of its extensive validation.
Condensation Index
See also Cond_HorizontalTube_avg
